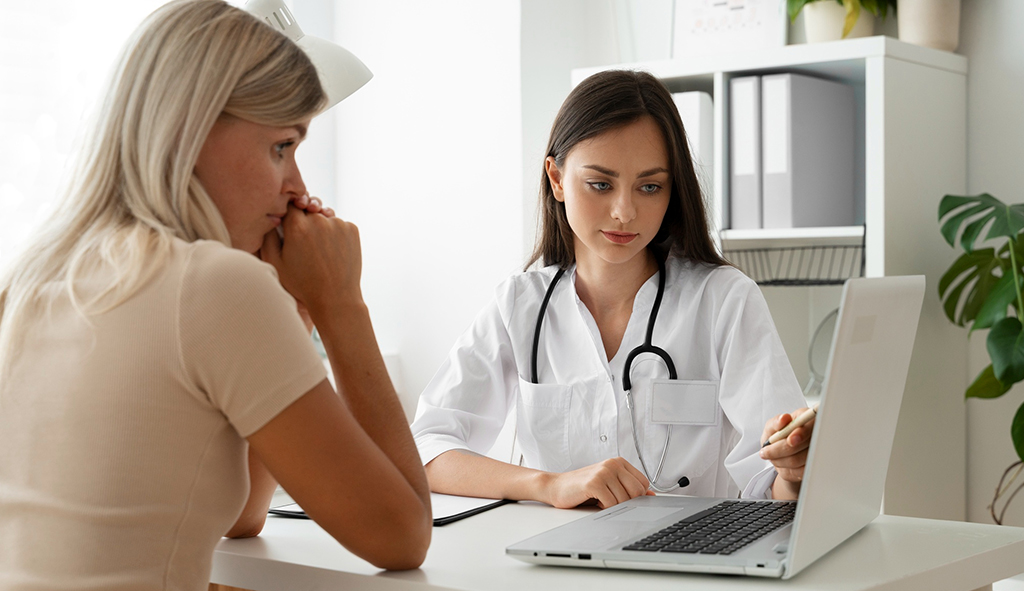
Good communication is fundamental to good healthcare. Most crucially, it serves as a bridge between the presentation of symptoms and accurate diagnosis, and between the establishment of treatment plan(s) and improvement/recovery.
So what happens when language actually becomes a barrier to quality care?
Imagine sitting in a doctor’s office, waiting for answers, only to be handed a medical report in a language you don’t understand. Or fretting at home the day before a procedure, because the critical pre-treatment guidelines you were given are not written in your native language. For millions of patients worldwide, such scenarios are a daily reality. Without access to comprehensible medical information, patients may struggle to describe their symptoms, follow treatment plans, or make truly informed decisions about their own care.
Breaking Down Language Barriers in Healthcare
For healthcare professionals, language barriers can be equally frustrating and worrisome. They can lead to missed appointments, treatment errors, and unnecessary complications. A patient who doesn’t understand their pre-surgery instructions may arrive unprepared. A prescription label that’s not written in a patient’s preferred language could result in a dangerous dosage mistake. A consent form riddled with unfamiliar terminology may leave patients unsure about the risks of a procedure.
These challenges can’t be adequately addressed in a series of quick fixes. For truly effective mitigation, they demand a structured approach to language access. By integrating professional translation services into key patient touchpoints, healthcare institutions can improve efficiency, reduce liability, and, most importantly, provide safer, more-equitable care.
Where Translation Makes a Difference
Strategic translation efforts can streamline workflows, improve patient engagement, and enhance overall healthcare outcomes. Here are some of the most critical areas where language support benefits both patients and healthcare providers:
1. Pre-Treatment Information
Before a procedure, patients need to follow specific instructions that often include fasting, avoiding certain medications, or preparing for anesthesia. When these guidelines are translated into a patient’s preferred language, misunderstandings on their end are minimized, which reduces the likelihood of last-minute cancellations or medical complications.
2. Consent Forms
Informed consent isn’t just a legal requirement, it’s a cornerstone of ethical medical practice. When consent forms are made available in multiple languages, patients can fully understand their treatment options and associated risks. This step not only protects patient rights, but also reduces legal risks for healthcare institutions.
3. Appointment Reminders
Missed appointments disrupt treatment schedules and waste valuable resources. By providing reminders in a patient’s native language—via text, email, or phone call—healthcare professionals can improve attendance rates and ensure that patients receive timely care.
4. Patient Education Materials
Empowering patients with knowledge leads to better health outcomes. Whether via brochures, digital content, or instructional videos, multilingual patient education materials help healthcare providers promote preventive care, reduce hospital readmissions, and foster trust with diverse patient populations.
5. Prescription and Medication Reminders
Medication adherence is critical to treatment success. When prescriptions, dosage instructions, and potential side effects are clearly translated into a patient’s preferred language, the risk of adherence errors decreases. Taking this step enhances patient safety, and supports pharmacists and healthcare teams in ensuring proper drug administration.
6. Post-Treatment Instructions
Following a medical procedure, patients are often given detailed recovery guidelines. Providing these instructions in their preferred language helps to prevent avoidable complications. Comprehensible instructions ensure that patients understand how to manage symptoms, take medications correctly, and recognize warning signs that require immediate attention.
7. Emergency Contact Information
When emergencies arise, fast and accurate communication is essential. Translated emergency contact details ensure that patients can reach the right healthcare professionals without delay. They can be critical in reducing response times and improving emergency care outcomes.
8. Health Portal Access
A multilingual health portal allows patients to view their medical records, lab results, and appointment schedules in their native language. This not only improves patient engagement but also reduces administrative burdens on staff members who might otherwise need to field repeated questions.
9. Patient Feedback and Satisfaction Surveys
Collecting patient feedback is key to improving healthcare services. By offering multilingual surveys, hospitals and clinics can gain valuable insights into patient experiences, identify gaps in care, and refine their communication strategies to better serve diverse populations.
The Future of Healthcare is Multilingual
As the global healthcare landscape continues to evolve in terms of both treatments and technology, the need for professional medical translation services is greater than ever. While AI-powered translation tools are helpful in assisting translators with meeting that demand, human expertise remains essential for ensuring accuracy, cultural sensitivity, and legal compliance in all patient interactions and related communications.
By prioritizing language access, healthcare institutions can break down communication barriers, improve patient outcomes, and build stronger relationships with the communities they serve. In the end, delivering high-quality care isn’t just about medical expertise—it’s about ensuring that every patient, regardless of the language they speak, receives the understanding and support they deserve.









