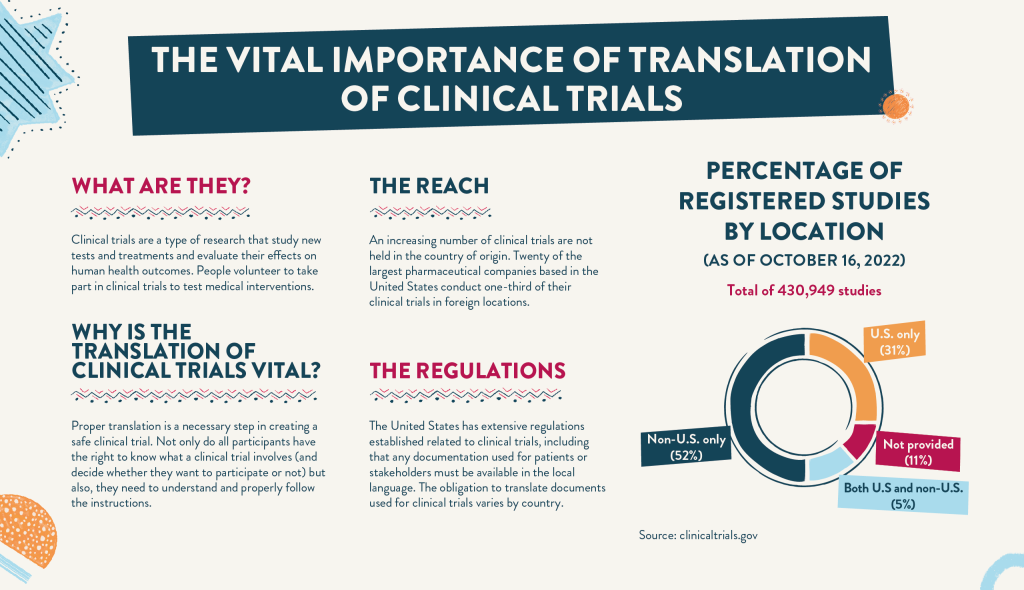
Multicultural consumers are the fastest growing segment in the U.S. according to a 2015 Nielsen report. Already over 120 million strong, this thriving sector increases by 2.3 million every year. Content must evolve to meet the language needs of the flourishing multicultural market and global economy. Businesses are now relying on translation companies to translate and interpret content to keep up with market demands.
There are many advantages to partnering with translation companies over translation alternatives such as using freelancers or Google Translate.
Quality of Translations

One of the major benefits from a translation company is the superior quality of work. Translation companies are distinguished by three components to ensure the highest of accuracy.
The first component is a Vendor Manager. Vendor Managers vet every linguist that joins the team to ensure they have all the qualifications needed for a specific project or vertical.
The second component is Project Manager (PM) and Account Manager (AM). The PM and AM oversee projects in a fashion dictated by the client. Often times the AM is client facing, communicating the desired language dialect, format, and timeline to the PM. The PM will identify the best linguist and subject matter expert for the project.
Lastly, the Sales team makes up the final component of a translation company. The Sales team does much more than negotiate deals. They have their finger on the pulse of many verticals and understand all the ins and outs of the language service industry. They convey the translation company’s strengths as well as address concerns or answer questions from prospects. With the guidance of the Sales team, prospects and clients will better understand the translation process and discover needs they didn’t know they had. The multiple points of contact positively impact the quality of work and ease of doing business.
Timeliness
Regardless of project size or complexity, a translation company can pick up nearly any new project and hit deadlines in a timely manner. A translation company has the structure and the bandwidth to handle new projects quickly. Turnaround time on projects can be completed faster if needed because more linguists may be placed on the project.
Specialized Linguists
Translation companies better handle highly technical industries. They often staff teams with technical knowledge in addition to their linguistic expertise. To work with linguists with this additional insight is a huge benefit to industries with complex scientific text or strict guidelines such as HIPPA laws.
Technology

A significant perk to using a translation company is the agency’s access to technology. Different translation companies will leverage technology to the client’s advantage. For example, AI and machine translation create efficiency when translating certain projects. Computer Assisted Translation (CAT) tools are another technology they will utilize to execute faster and more accurate translations. The more work the CAT tool is fed, the more accurate translations will become. From graphics to recordings, translation companies usually have the technology and equipment available to produce all desired deliverables. Finally, translation companies have the ability to provide additional complementary services that other translation alternatives can not. This includes proofreading, in-country review, quality control, DTP, and voice-overs. This again streamlines the process and makes a translation company a one-stop-shop for all translation needs.